The introduction of UAE Corporate Tax on Foreign Income has currently extensively reshaped the taxation landscape for both the resident and nonresident with a Permanent Establishment (PE) within the UAE. Understanding the tax treatment of foreign income is important for businesses and individuals working in or with the UAE, in particular with international operations or cross-border activities. This blog will discuss the key insights and implications of UAE Corporate tax law on foreign income.

What Constitutes Foreign Source Income Under UAE CT Law?
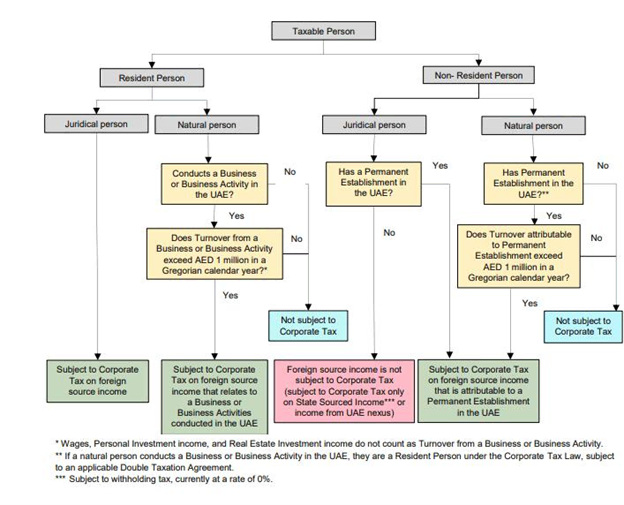
(Source – Guide on Taxation of Foreign Source Income issued by Federal Tax Authority)
Under the UAE Corporate Tax Law, foreign source income refers to income derived from activities, assets, or services outside the UAE. This includes earnings from foreign companies, dividends from non-UAE entities, proceeds from the sale of foreign assets, royalties, and interest from foreign investments. In essence, any income that originates outside the UAE and is delivered into the USA is classified as foreign source income.
However, income derived from business or investments located within UAE Free Zones is not considered a foreign source income. These incomes are assessed as domestic-source income. Similarly, if a UAE-primarily based enterprise has a Foreign Permanent Establishment (PE), the income generated via that PE is treated as foreign source income, subject to relevant tax exemptions and provisions under the Corporate Tax Law.
Who Is Liable for Tax on Foreign-Source Income?
The tax liability for foreign source income depends on the residence status of the entity or individual generating the income.
- Resident Companies:
Resident companies within the UAE are concerned with corporate tax on each domestic and foreign supply income. This consists of entities that are incorporated or managed in the UAE. The tax treatment of foreign source income consists of exemptions designed to mitigate double taxation. These exemptions are important in making sure that businesses do not face double taxation on the ame income—as soon as withinside the foreign jurisdiction and once more withinside the UAE.
- Non-Resident Companies:
Non-resident companies are the most effective concern for corporate tax on foreign source income if they have a permanent establishment (PE) inside the UAE. The income generated via this PE is handled as taxable income within the UAE. If a non-resident entity operates without a PE inside the UAE, its foreign source income is commonly no longer subjected to UAE tax.
- Resident Natural Persons (Individuals):
natural persons who are citizens of the UAE are taxed on foreign source income, only if it’s far linked to their business activities in the UAE. However, this applies only if the individual annual turnover exceeds AED 1 million. Foreign income unrelated to their UAE-based business activities aren’t taxed withinside the UAE. Personal investment income and income from real-estate investments abroad remain exempt from corporate tax.
- Non-Resident Natural Persons:
Non-resident individuals are subjected to corporate tax on foreign source income, only if they have a permanent establishment inside the UAE or if their business activities meet the threshold of generating an annual turnover exceeding AED 1 million. If those situations aren’t met, their foreign income remains untaxed inside the UAE.
Exemptions and Double Taxation Relief
The UAE has applied numerous exemptions to reduce or eliminate the risk of double taxation. Key exemptions consist of:
- Participation Exemption: This exemption applies to income derived from a UAE entity’s shareholding in foreign companies.
- Foreign Permanent Establishment Exemption: If a business has a PE abroad, its foreign source income generated via that PE can be exempt from UAE tax.
Additionally, the UAE Corporate Tax Law gives a foreign tax credit to mitigate double taxation. If foreign source income is a concern to tax in any other jurisdiction, businesses may be able to claim a credit score for the foreign taxes paid, decreasing their UAE tax liability.
When Is Foreign-Source Income Taxable Inside the UAE?
For companies, the tax period for foreign source income aligns with the same standard financial year or 12-month duration for which financial statements are prepared. In contrast, for natural persons, the tax-period is generally the Gregorian calendar year. This determines the timing of when foreign source income will become taxable beneath the UAE Corporate Tax Law.
How Is Foreign-Source Income Taxed?
Foreign-source income is taxed primarily based on the same principle as domestic income within the UAE. Both income and deductible fees from domestic and foreign assets are consolidated to calculate the taxable income. This permits businesses to offset losses from foreign operations against domestic income, except for any expenses associated with exempt income (like foreign dividends that qualify for participation exemptions).
Moreover, businesses with total revenue (domestic plus foreign) under AED 3 million can also additionally use the cash basis of accounting, which could simplify the taxation system.
Tax Rates for Foreign-Source Income
Foreign-source income is a concern to the same corporate tax rates as income generated in the UAE, with the subsequent structure:
- 0% for taxable income up to and including AED 375,000.
- 9% for taxable income exceeding AED 375,000.
This revolutionary tax system guarantees that small businesses with restrained income aren’t overburdened by tax liabilities, while large businesses make a proportionately greater contribution.
Conclusion
The taxation of foreign source income beneath the UAE Corporate Tax Law is a complex but manageable system for both businesses and individuals. The tax treatment varies depending on the residence status of the taxpayer and the nature of the income. However, the UAE’s system of exemptions, in conjunction with the opportunity of foreign tax credits, guarantees that businesses aren’t double taxed at the identical income. For companies and individuals with cross-border activities, knowing those policies is important to make sure of compliance and optimize tax liabilities.
By implementing those regulations, the UAE aims to create a more transparent and business-friendly tax environment at the same time as retaining its status as a global enterprise hub. For companies and individuals conducting global operations, the new UAE Corporate Tax Law on foreign income gives a clear and structured framework for managing foreign source income taxation.
A corporate tax consultant in dubai can help businesses in navigating the complexities of UAE Corporate tax law foreign source income. They help companies in providing expert advice on exemptions, foreign tax credits and cross-border taxation strategies
FAQs
Is foreign income taxed under UAE Corporate Tax?
Foreign income may be subject to UAE Corporate Tax depending on its source and compliance with tax regulations.
What is the tax rate for foreign income in the UAE?
The UAE imposes corporate tax on foreign income at rates defined by the specific rules under UAE tax law.
Are there exemptions for foreign income under UAE tax?
Yes, certain foreign income may be exempt if it meets specific criteria under the UAE Corporate Tax law.
How does UAE Corporate Tax on foreign income affect my business?
It can impact your tax obligations, requiring businesses to adjust to new regulations and ensure proper compliance.

